Sarcolemma Diagram Quizlet
Sarcolemma hires stock photography and images Alamy
Excitation-contraction coupling is the physiological process of converting an electrical stimulus to a mechanical response. It is the link (transduction) between the action potential generated in the sarcolemma and the start of a muscle contraction. Figure 38.19.1 38.19. 1: Excitation-contraction coupling: This diagram shows excitation.

Image result for Sarcolemma Actin Myosin . Sarcoplasmic reticulum Skeletal muscle
Stavba kosterní svaloviny. Jádra jsou oválná, nachází se na periferii těsně pod povrchem. Plazmatická membrána, zde nazývána sarkolema, vytváří tubulózní invaginace - T-tubuly. Na povrchu vlákna je komplex lamina basalis a sítě retikulárních vláken = endomysium; celý komplex sleduje sarkolemu i do lumina T-tubulů.

Image result for sarcoplasmic reticulum
ACh is the neurotransmitter that binds at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) to trigger depolarization, and an action potential travels along the sarcolemma to trigger calcium release from the SR. The myosin binding sites on actin sites are exposed after calcium enters the sarcoplasm and activates the troponin-tropomyosin complex to shift.

Pin by Aline on Biology Muscular system anatomy, Exercise physiology, Muscle structure
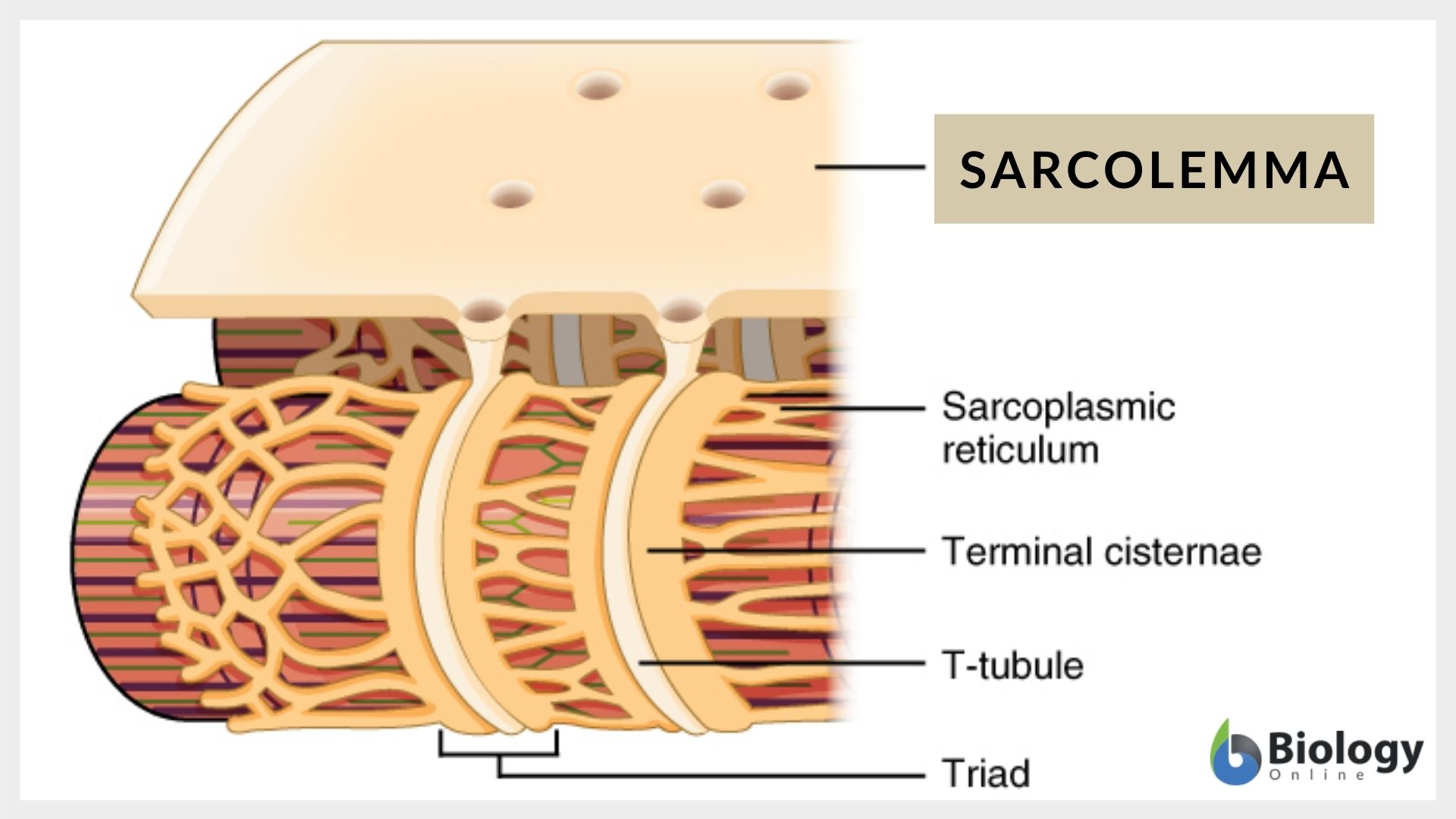
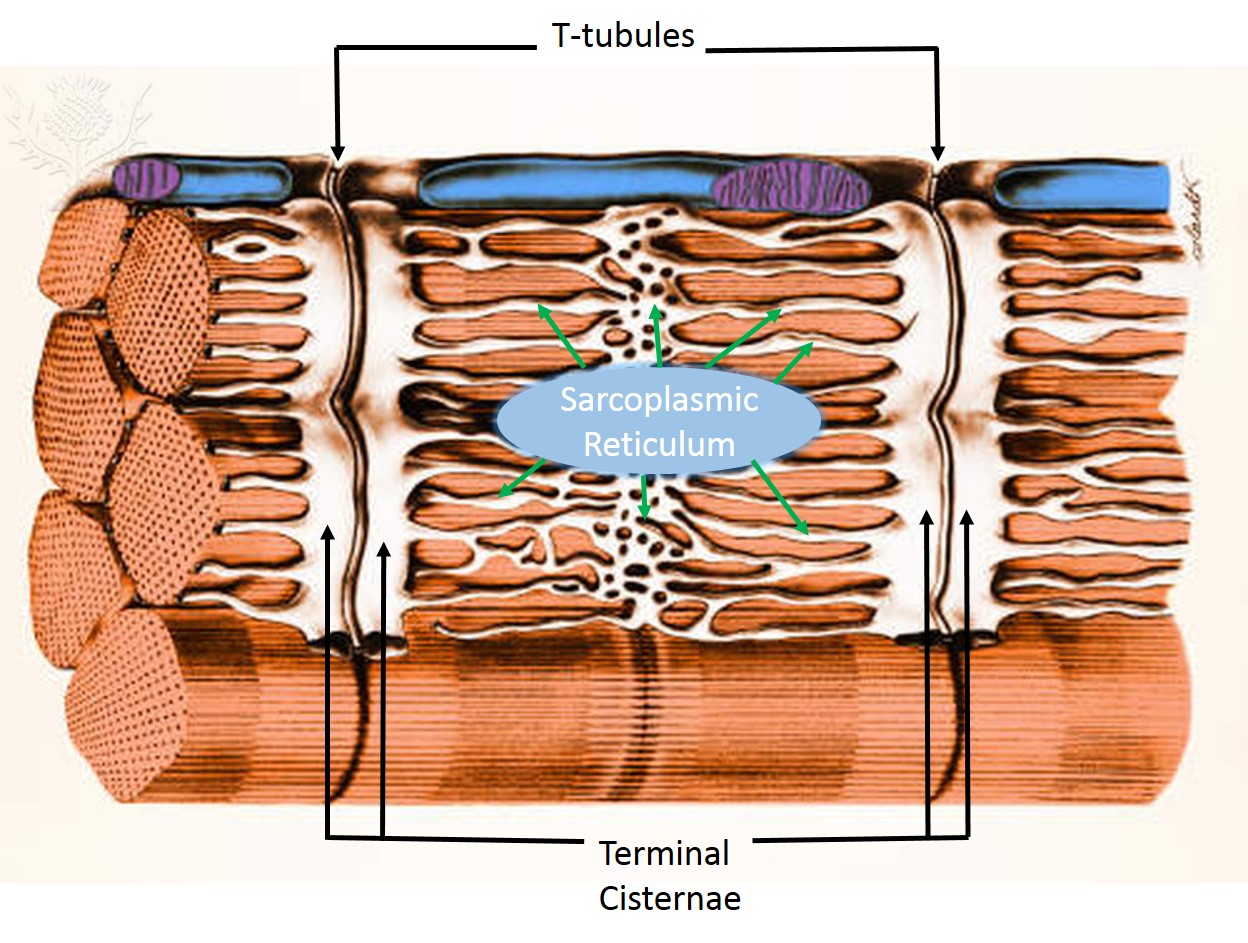
Sarcolemma. The sarcolemma or cell membrane is the site where calcium enters and leaves the cell through a distribution of ion channels, transporters, and pumps. The T-tubules are invaginations of the sarcolemma that form a permeability barrier between the cytosol and the extracellular space (Brette and Orchard, 2003).

Sarcolemma and Ttubules Diagram Quizlet
The sarcolemma has several unique characteristics that provide the muscle cells with the structure and the resources to function. The sarcolemma is very large compared to some cell membranes and must be constantly maintained to cover the many myofibrils that make up a muscle cell. The sarcolemma of a cell adheres through extracellular.

Sarcolemma Diagram Quizlet
Excitation-contraction coupling is the link (transduction) between the action potential generated in the sarcolemma and the start of a muscle contraction. The trigger for calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the sarcoplasm is a neural signal. Each skeletal muscle fiber is controlled by a motor neuron, which conducts signals.
Sarcolemma Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
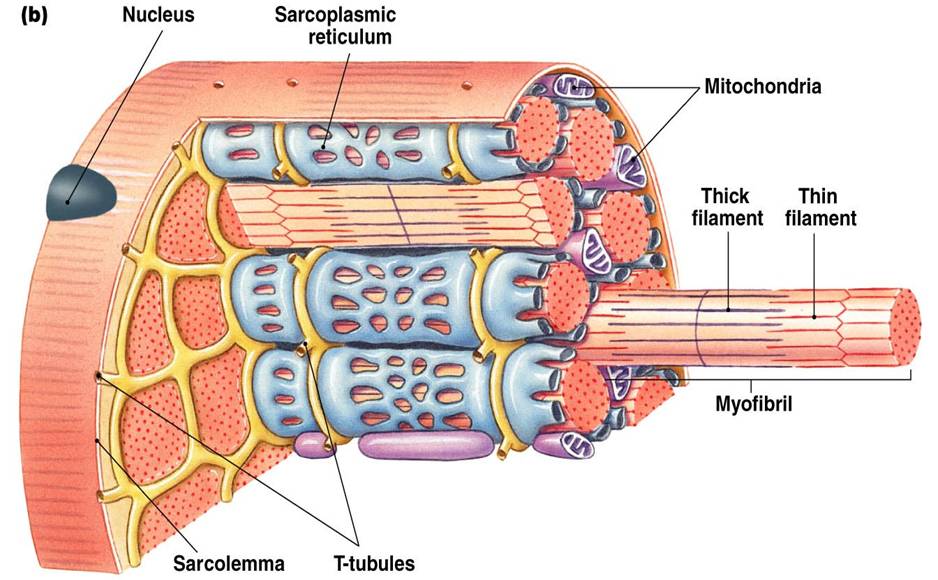
Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. Skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. Skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. The membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm.

Sarcolemmal proteins and structure. (A) The DAPC is a... Download Scientific Diagram
The sarcolemma is the plasma membrane. The sarcolemma is described as having two layers. The first is the plasma membrane, which is a structure of similar biochemical composition to the general plasma membrane found in eukaryotic cells. The second layer is the glycocalyx, which is in contact with the basement membrane.
Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review
Sarcolemma is the outermost layer of the muscle fibre that separates the sarcoplasm from the extracellular surroundings. It contains a network of fibrils, a foundation membrane and a network of ion-specific channels that support the electrical activity of the muscle fibre. Learn more about sarcolemma in muscle anatomy, heartbeat, muscle disease and other topics.

JCI Insight Stabilization of the cardiac sarcolemma by sarcospan rescues DMDassociated
The sarcolemma is the fine, delicate, extensible membrane surrounding each muscle fiber. It is composed of a cell, or plasma, membrane which presents an extracellular matrix of collagen fibrils and polysaccharides that make contact with the basal lamina. The sarcolemma also contains tunnel-like invaginations into the sarcoplasm, which are known.

Sarcolemma Structure Muscle Fiber Educational Closeup Stock Vector (Royalty Free) 2258898069
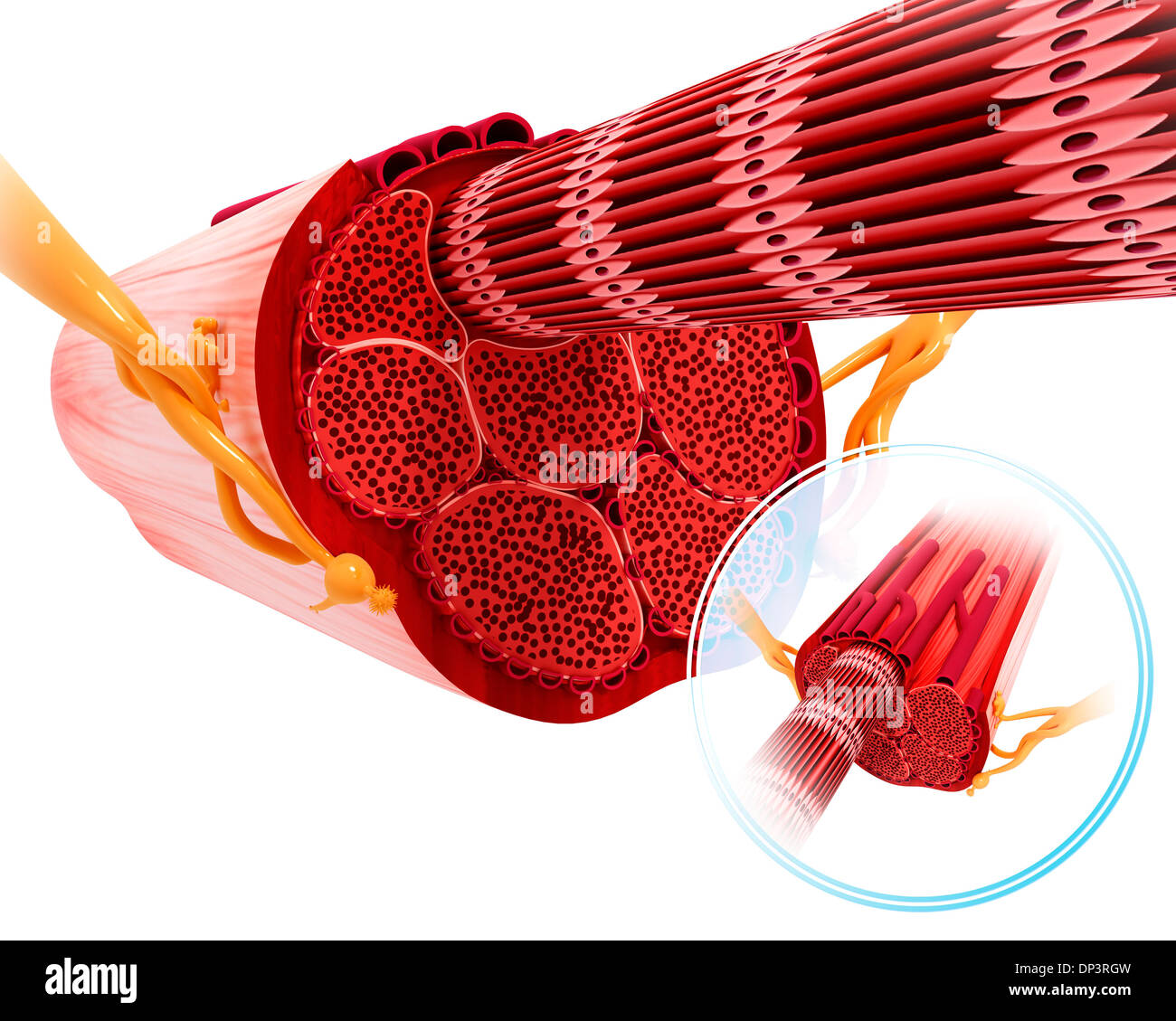
1. Just to illustrate Gerardo's answer, this picture is provided. The endomysium as you see is a layer of connective tissue which surrounds the individual muscle fibres (cells) (in between one muscle cell and the next) but each muscle cell in particular is lined or covered by a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma. Share.

Human Physiology Muscle
The postsynaptic muscular membrane (sarcolemma) is covered, on the extracellular surface, with a layer of electron-dense material, the basal lamina (Figure 6.12 a,c). This lamina, which follows the folds of the sarcolemma, is a conjunctive tissue secreted by the non-myelinating Schwann cells covering the axon terminals.

Muscle Membrane Sarcolemma Anatomical Structure Outline Stock Vector (Royalty Free) 2116902443
Skeletal muscle histology. This type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. Skeletal muscle is an excitable, contractile tissue responsible for maintaining posture and moving the orbits, together with the appendicular and axial skeletons. It attaches to bones and the orbits through tendons.
What Is The Function Of The Sarcoplasmic Reticulum In Skeletal Muscle
sarcolemma: [noun] the membrane enclosing a striated muscle fiber.

What is the Difference Between Sarcolemma and Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Cell
Sarkolema atau miolema adalah kulit luar urat yang sangat tipis, dan memiliki bentuk menyerupai pembuluh. Sarkolema terdiri dari membran sel disebut juga membran plasma, dan sebuah lapisan luar yang terdiri dari satu lapisan tipis bahan polisakarida yang mengandung sejumlah serat kolagen tipis. Pada ujung serat otot, lapisan permukaan sarkolema bersatu dengan serat tendon.

Review for Final at Hillsborough Community College StudyBlue
Sarcolemma is a specialized cell membrane that surrounds striated muscle fiber cells. It has channels for glucose, nutrients, and ions to enter and exit the cell, and connects the basement membrane and other muscle cells. It also contains proteins to control the cell's functions and responses.